In the fields of immunology and inflammatory disease research, cytokines play a pivotal role. Among them, TNFα and IL-6, as two core inflammatory markers, are not only involved in regulating immune responses but also closely associated with the development and progression of various diseases. With the rapid advancement of biomedical technologies, detection methods for TNFα and IL-6 have also undergone continuous innovation. Today, we will delve into the significance of these two cytokines, their detection methods, and their application value in research and clinical settings.
TNFα: The "Double-Edged Sword" of Inflammatory Responses
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) is primarily secreted by activated macrophages, T cells, and other immune cells, serving as a key regulator in inflammatory responses. It can both promote the activation and proliferation of immune cells and induce apoptosis, playing a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis. However, excessive expression of TNFα is closely linked to diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and cancer. Currently, anti-TNFα therapies have become an important treatment approach for these conditions, with drugs like infliximab and adalimumab widely used in clinical practice.
IL-6: The "Magic" of a Pleiotropic Cytokine
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine involved in regulating immune responses, acute-phase reactions, and hematopoiesis. By binding to its receptor (IL-6R), IL-6 activates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, influencing B cell differentiation, T cell function, and inflammatory responses. In recent years, IL-6 inhibitors (such as tocilizumab) have demonstrated significant efficacy in treating rheumatoid arthritis and cytokine release syndrome, making IL-6 a hot target in the biomedical field.
In research and clinical settings, accurately measuring the concentrations of TNFα and IL-6 is crucial for disease diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and drug development. Currently, commonly used detection technologies include ELISA, TR-FRET, MSD, and Luminex, each with its own advantages and limitations.
1. ELISA: Classic but Cumbersome
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a well-established detection method known for its high sensitivity and low cost. However, its operation involves multiple washing steps, and its throughput is relatively low, making it unsuitable for high-throughput screening.
2. TR-FRET: The Marriage of Efficiency and Precision
TR-FRET (time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer) technology detects targets through energy transfer between fluorescent donors and acceptors, offering the following advantages:
High Sensitivity and Wide Linear Range: Capable of detecting cytokines at concentrations as low as pg/mL, suitable for analyzing samples across a broad concentration range.
High Throughput: Compatible with 384-well or even 1536-well plates, significantly improving detection efficiency.
Easy to use: Homogeneous detection without washing steps reduces human error.
3.MSD and Luminex: Powerful Tools for Multiplex Detection
MSD (electrochemiluminescence) and Luminex support multiplex cytokine detection, making them ideal for analyzing complex samples. However, their high instrument costs and complex operations make them more suitable for large laboratories or clinical research.
Technology Comparison Summary:
Technology | Sensitivity | Flux | User-friendly Control | Cost |
ELISA | High | Low | Medium | Low |
TR-FRET | Extremely high | High | High | Medium |
MSD/Luminex | Extremely high | High | low | High |
Technical Principle
KeyTec® TR-FRET technology employs a pair of specific antibodies labeled with donor (Solar Eu) and acceptor (LA) fluorescent groups. When the antibodies bind to the target cytokine, the donor and acceptor come into proximity, enabling energy transfer. Quantitative analysis is achieved by detecting fluorescence signals at specific wavelengths.
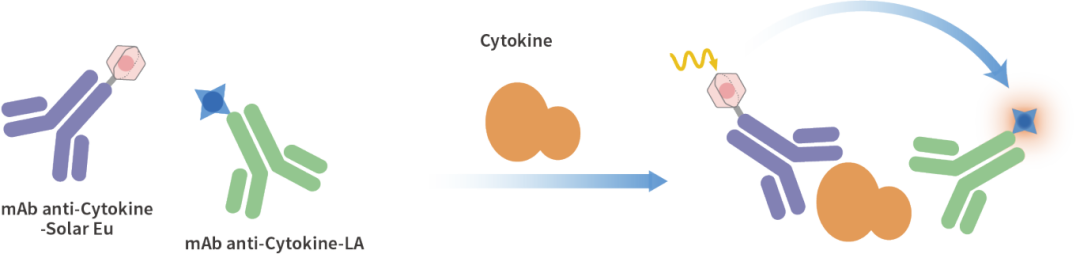
KeyTec® TR-FRET Cytokine Detection Principle
Core Advantages
High Sensitivity and Specificity: Enables precise detection of low-concentration cytokines in complex samples.
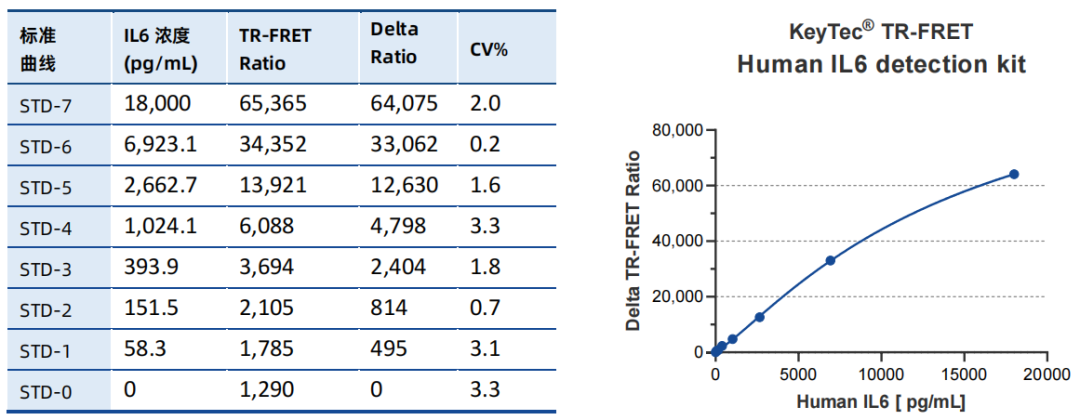
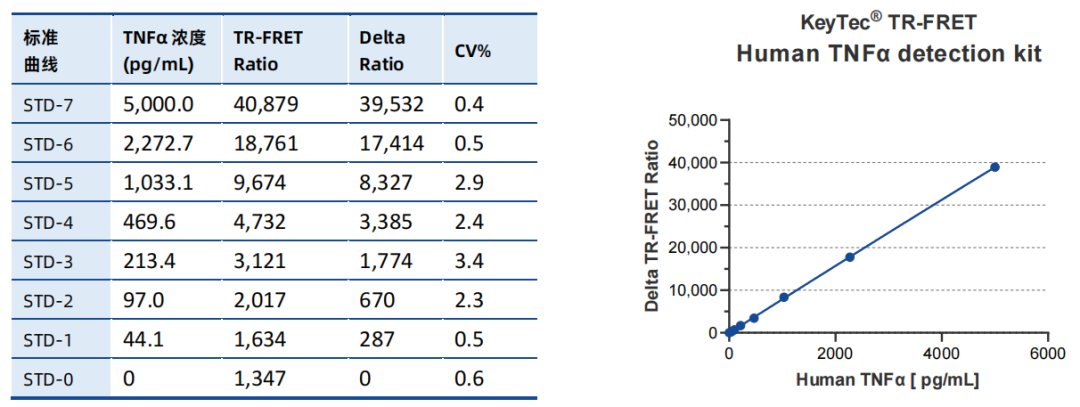
Wide Dynamic Range: Broad linear range (IL-6: 26–18,000 pg/mL; TNFα: 30–5,000 pg/mL), suitable for samples with varying concentration gradients.
High Throughput Compatibility: Supports 384-well plate detection, meeting the needs of drug screening and clinical research.
Easy to use: No washing steps required; direct detection of cell supernatants saves time and effort.
Data Presentation
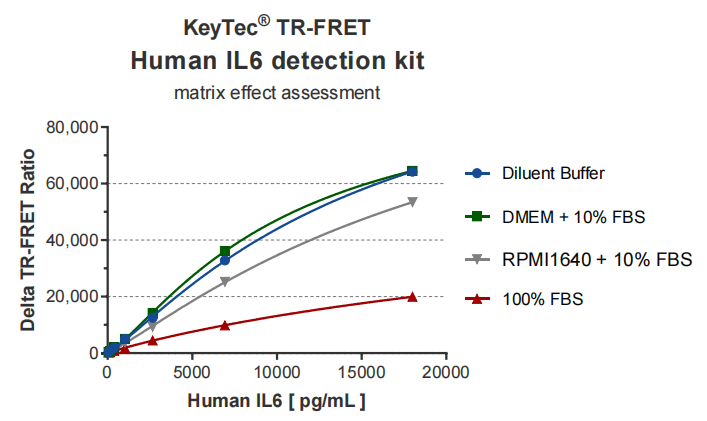
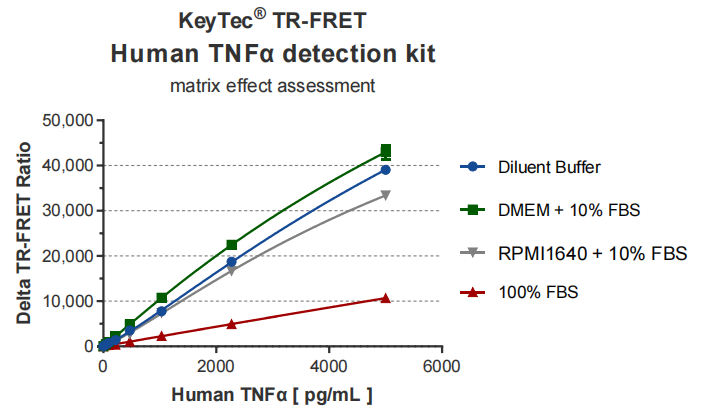
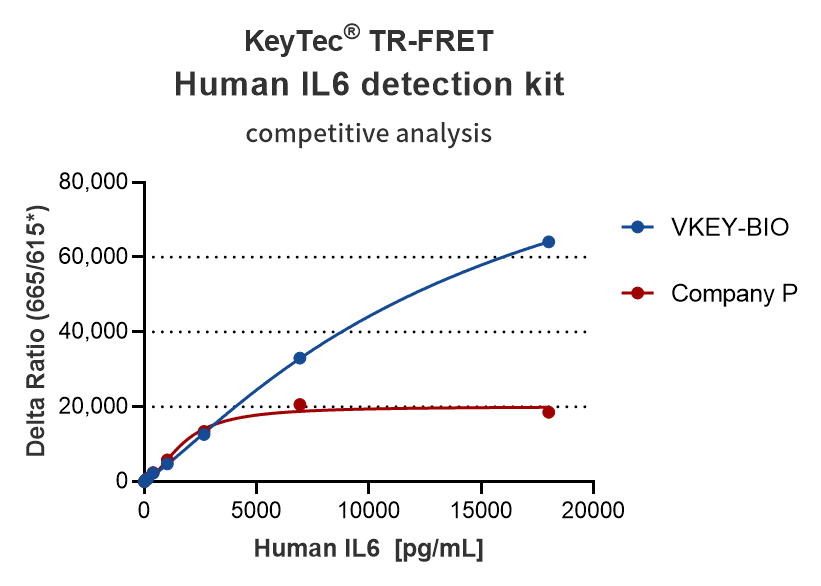
KeyTec® TR-FRET kits demonstrate excellent linearity (R² > 0.99) in standard curve tests and maintain stability across different buffers, with signal values significantly outperforming competitors. These features make them an ideal choice for both research and industrial applications.
KeyTec® TR-FRET Human IL-6 Cytokine Detection Standard Curve:
KeyTec® TR-FRET Human TNFα Cytokine Detection Standard Curve:
KeyTec® TR-FRET IL-6/TNFα Cytokine Buffer Detection Results:
KeyTec® TR-FRET TNFα Cytokine Competitor Comparison Results:
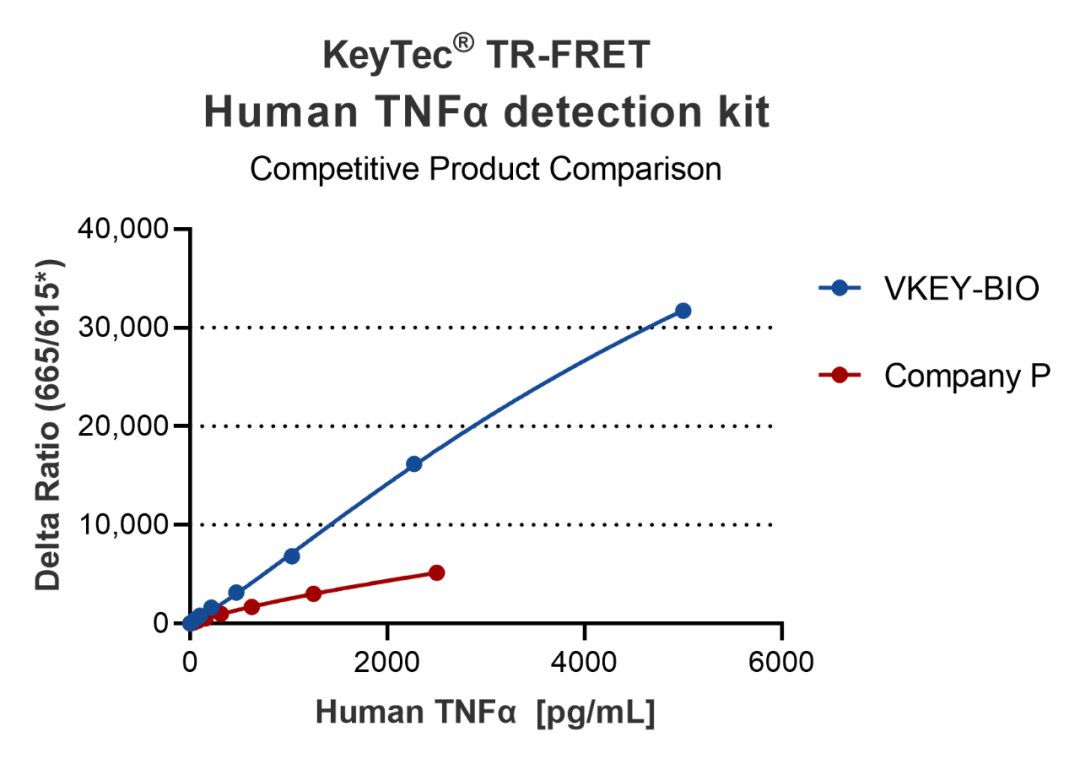
Application Scenarios
Drug Development: High-throughput screening and efficacy evaluation of anti-TNFα or IL-6 drugs.
Basic Research: Exploration of immune regulation mechanisms and molecular foundations of disease development.
Product Recommendations
VKEY-BIO offers a comprehensive series of TR-FRET cytokine detection kits to help you tackle research challenges with ease:

As the era of precision medicine unfolds, cytokine detection technologies will continue to evolve toward higher sensitivity, broader detection ranges, and lower costs. TNFα and IL-6, as the core regulatory factors of inflammation and immunity, the advancement of their detection technologies will directly promote the research and treatment of related diseases. KeyTec® TR-FRET technology, with its efficiency, precision, and user-friendliness, is emerging as the new benchmark in cytokine detection. Choose VKEY-BIO to make research simpler and the future more precise!
References
1. Idriss HT, Naismith JH. TNF alpha and the TNF receptor superfamily: structure-function relationship(s). Microsc Res Tech. 2000.
2. Neurath MF, Finotto S. IL-6 signaling in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011.