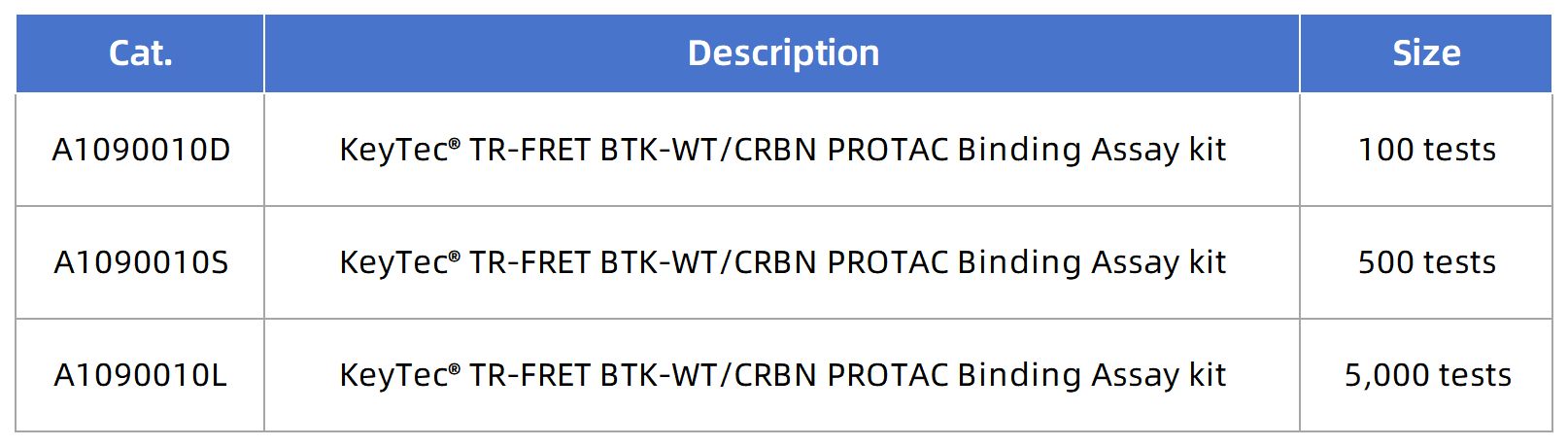
In the field of targeted cancer therapy, PROTAC (Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera) technology is leading a revolutionary paradigm shift. Unlike traditional small molecule inhibitors, PROTAC molecules act like a "molecular bridge": one end binds to the target protein, while the other recruits an E3 ubiquitin ligase, directing the target protein to the ubiquitin-proteasome system for degradation, thereby eliminating disease-associated proteins at their source (Figure 1). This mechanism brings new hope for many traditionally "undruggable" targets and demonstrates great potential in overcoming drug resistance.
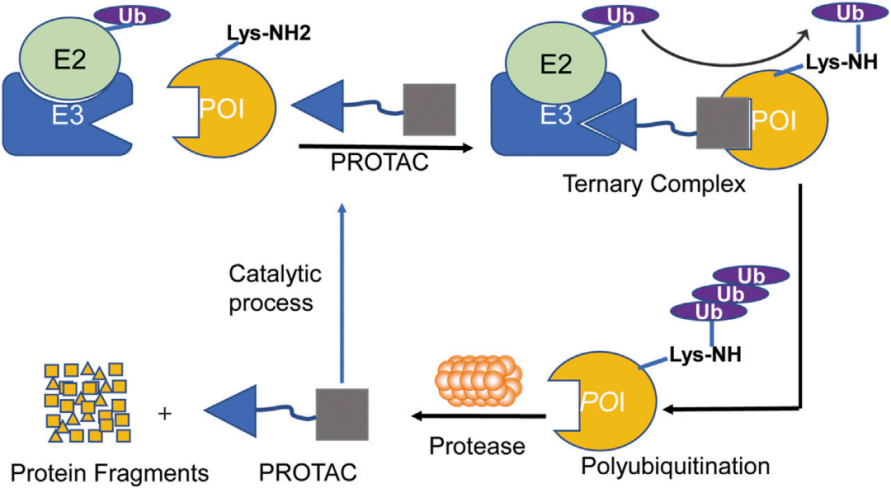
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of PROTAC-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of target proteins (Source: doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.692574)
Among the numerous targets of great interest, BTK (Bruton's tyrosine kinase), a core component of the B-cell receptor signaling pathway, is closely associated with the development and progression of various B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma, through its aberrant activation. Consequently, BTK has become a validated gold-standard target in hematological cancer therapy. Developing PROTAC molecules capable of efficiently degrading BTK holds promise for offering new therapeutic strategies for patients who are unresponsive or resistant to existing treatments.
The core efficacy of a PROTAC molecule depends on its ability to stably form the "Target Protein-PROTAC-E3 Ligase" ternary complex. However, traditional methods for detecting ternary complexes (such as co-immunoprecipitation, gel shift assays, etc.) are cumbersome, low-throughput, and difficult to quantify, severely hindering the efficiency of early-stage PROTAC screening and optimization.
Addressing the multi-layered needs in PROTAC R&D, VKEY-BIO, leveraging its mature KeyTec® TR-FRET technology, introduces a comprehensive detection solution covering the entire R&D chain:
Target-Ligand Binding Assay (Binary Complex): Precisely evaluates the direct affinity between ligands and target proteins or E3 ligases.
* Human Cereblon Binding Assay Kit
* Human VHL Binding Assay Kit
Core PROTAC Efficacy Assay (Ternary Complex): Directly and quantitatively characterizes the "bridging" function of PROTAC molecules, assessing ternary complex formation capability.
* STAT6/CRBN PROTAC Binding Assay Kit
* BTK-WT/CRBN PROTAC Binding Assay Kit
The KeyTec® TR-FRET Solar Eu-conjugated anti-Tag1 antibody specifically recognizes Tag1-BTK WT protein. The KeyTec® TR-FRET LA-conjugated anti-Tag2 antibody specifically recognizes the Tag2-CRBN/DDB1 protein complex. Tag1-BTK WT protein and Tag2-CRBN/DDB1 protein complex can form a ternary complex mediated by the positive control PROTAC molecule MT-802, thereby bringing Solar Eu and LA into close proximity. Upon excitation by an external light source, resonance energy transfer occurs between the donor and acceptor. Detecting the signal intensity at a specific wavelength (665 nm) allows for the measurement of PROTAC molecule-mediated binding between BTK WT and CRBN/DDB1.
BTK-WT/CRBN PROTAC Binding Assay Principle
* Simple Operation, Fast Workflow: No wash steps required; a true homogeneous "Add-Incubate-Read" assay. The entire experimental procedure can be completed within hours.
* High Sensitivity, Wide Dynamic Range: Capable of detecting binding changes as low as nanomolar (nM) levels. The standard curve covers a broad range, meeting the detection needs for PROTAC molecules with varying affinities.
* Accurate Data, Excellent Reproducibility: The ratio-metric signal based on TR-FRET effectively overcomes inter-well variations, fluorescence quenching, and other interferences, resulting in low CV% and stable, reliable results.
* High-Throughput Compatibility: Optimized for 384-well microplates with a reaction volume as low as 20 µL, significantly saving precious samples and reagent costs, and perfectly compatible with automated workstations.
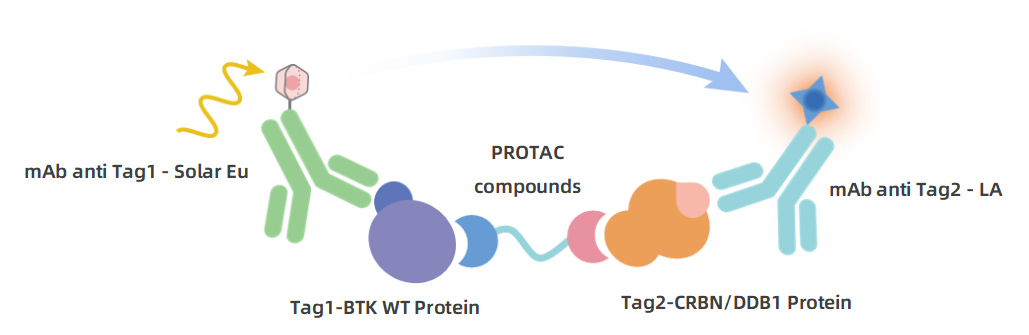
The kit includes the positive control PROTAC molecule MT-802. As shown in the figure, under standard experimental conditions, the TR-FRET signal exhibits a typical dose-dependent "bell-shaped" curve with increasing MT-802 concentration. This not only visually demonstrates the PROTAC's ability to induce ternary complex formation but also allows for the calculation of the EC₅₀ and the optimal concentration for achieving maximum binding (peak).
Experimental data show that this system has a high signal-to-background ratio (S/B) and low inter-well coefficient of variation (CV%), fully demonstrating its excellent assay stability and reproducibility, ensuring the reliability of screening results.