Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a crucial intracellular second messenger involved in regulating various physiological processes, such as metabolism, secretion, and gene expression. In drug development and basic research, accurately detecting cAMP levels is essential for understanding G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling pathways and screening targeted drugs. However, traditional detection methods (e.g., ELISA, radioimmunoassay) are often cumbersome and have narrow dynamic ranges, making them unsuitable for high-throughput, high-precision research needs. The KeyTec® TR-FRET cAMP Detection Kit leverages time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) technology, combining specific antibodies with fluorescent labels to achieve wash-free, highly sensitive detection of cAMP in cell lysates.
VKEY-BIO innovatively offers three tr fret assay kit, each designed with unique fluorescent labeling technology to provide precise solutions for different concentration ranges and experimental requirements:
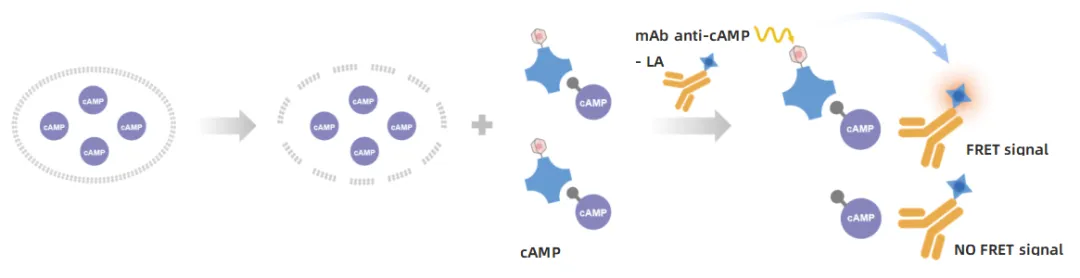
Principle: Utilizes a competitive "antibody-label" approach, where a specific antibody conjugated to a TR-FRET acceptor (LA) competes with biotinylated cAMP-donor (Solar Eu) complexes for binding.
Features: High-sensitivity design, ideal for detecting subtle signal changes.
Typical Applications: Gs receptor inhibition assays, weak agonist screening, and other low-concentration scenarios.
Wide-Range Kit
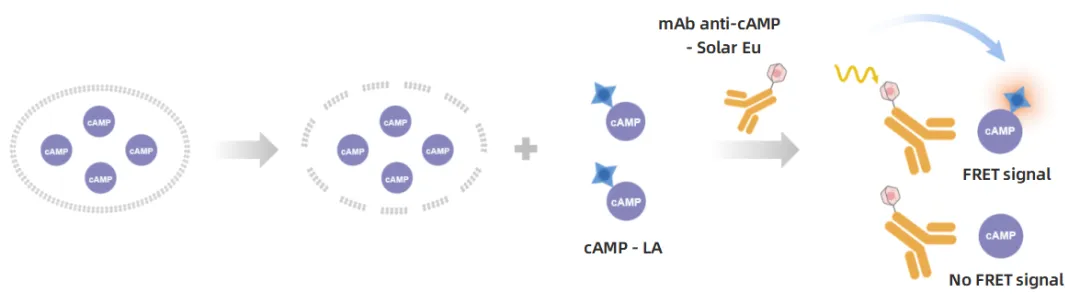
Principle: Optimizes antibody and cAMP direct conjugation strategies (mAb-Solar Eu vs cAMP-LA), expanding the detection range by adjusting conjugate ratios.
Features: Dynamic range of up to 4 orders of magnitude while maintaining high signal-to-noise ratios.
Typical Applications: Gs receptor strong activation, Forskolin stimulation, and other high cAMP-generation experiments.
Ultra-Wide Detection Kit
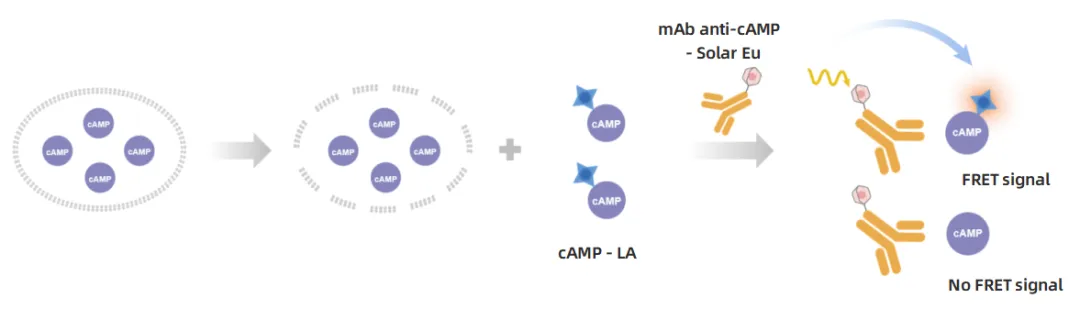
Principle: Builds on the Wide-Range Kit with further optimized label stability formulations, specifically enhancing detection linearity in high-concentration ranges.
Features: Reliable detection of high-concentration samples.
Typical Applications: Pathological models (e.g., tumors), cAMP detection under extreme stimulation conditions.
✅ High Sensitivity and Wide Dynamic Range
The kits employ unique fluorescent labeling technology, achieving a signal-to-background ratio (S/B) of over 20, ensuring precise detection of low cAMP concentrations. The wide dynamic range design eliminates the need for tedious sample dilution.
✅ Simple and Efficient Operation
From cell stimulation to data acquisition, the process takes only 1–2 hours and requires no complex washing steps, significantly improving experimental efficiency.
✅ Excellent Reproducibility and Stability
Stringent quality control standards and optimized buffer systems ensure minimal batch-to-batch variation and reliable data.
✅ Flexible Adaptation to Various Experimental Scenarios
Compatible with 96-well, 384-well, and 1536-well plates, allowing reaction system adjustments based on experimental needs. Suitable for diverse cell models, including GPCR agonist/antagonist screening, drug discovery reagents evaluation, and drug mechanism studies.
GPCR Signaling Pathway Research: Measure EC50/IC50 of agonists/antagonists.
Drug Screening and Optimization: High-throughput screening of small-molecule drugs, antibodies, or peptides targeting GPCRs.
Cell Model Validation: Evaluate the effects of candidate drugs and optimize cell stimulation conditions.
Disease Mechanism Research: Investigate abnormal cAMP pathway regulation in models of tumors, metabolic diseases, etc.
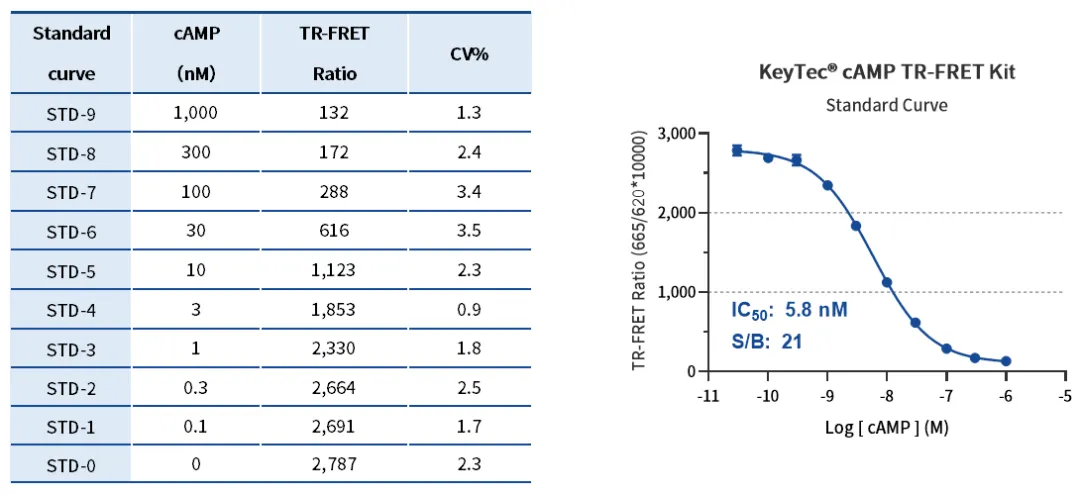
Standard Curve Results (Classic Kit)
Dynamic range: IC20–IC80.
IC50: 5.8 nM, indicating high sensitivity in the medium concentration range.
Signal-to-background ratio (S/B): 21, demonstrating high signal-to-noise for low to medium cAMP concentrations.
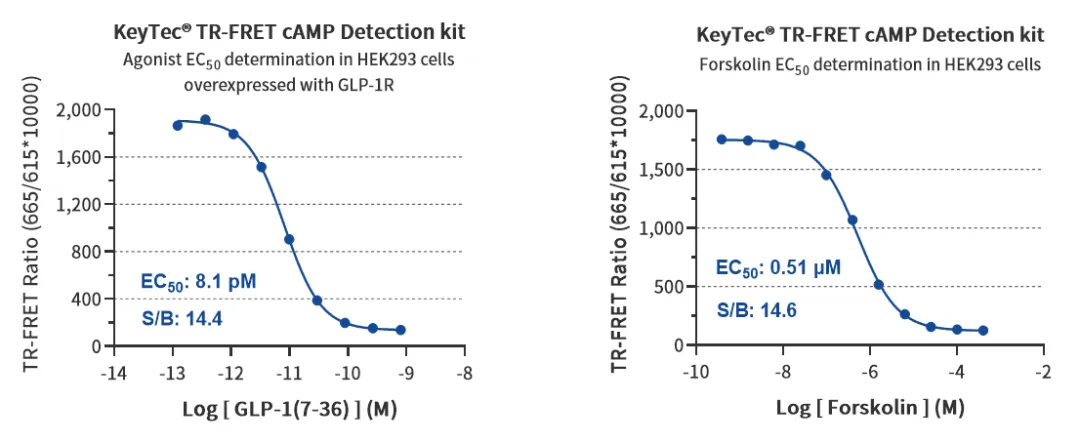
GLP-1R Agonist Assay (HEK293 Cells)
EC50: 8.1 pM, indicating extremely potent activation of GLP-1R by GLP-1(7-36).
S/B: 14.4, showing a good detection window.
Forskolin Activation Assay (HEK293 Cells)
EC50: 0.51 μM, precisely measuring Forskolin’s effect on adenylate cyclase activation.
S/B: 14.6, confirming kit reliability in cell models.
Comparison Data of the Three Kits:
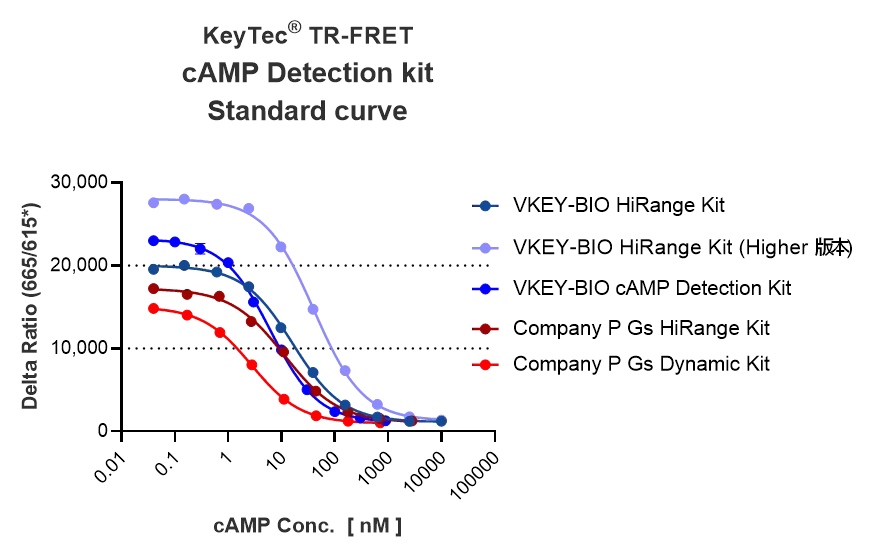
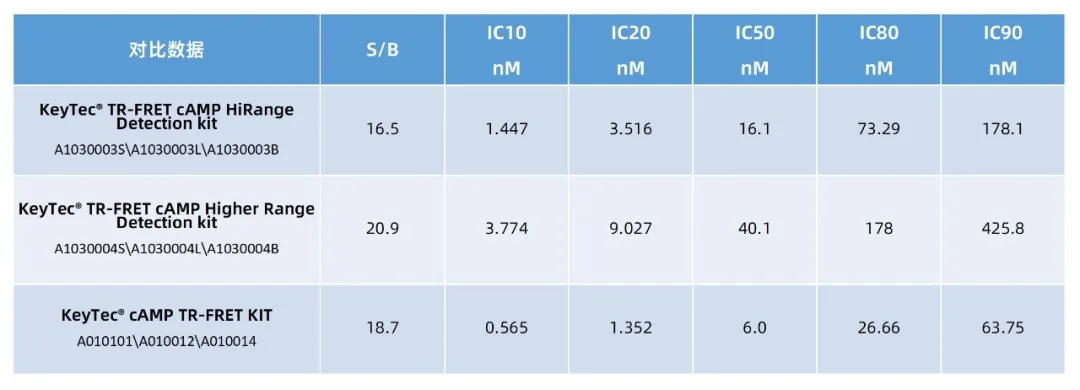
Classic Kit
Core advantage: High sensitivity (IC50 6.0 nM, S/B >20), precise detection of low cAMP concentrations.
Typical applications: Routine GPCR research (e.g., Gs inhibition, weak agonist screening), basic signaling pathway analysis.
Wide-Range Kit
Core advantage: 4-order dynamic range (IC50 16.1 nM), eliminating the need for sample dilution.
Typical applications: Strong Gs agonists, Forskolin stimulation, and other high cAMP-generation experiments.
Ultra-Wide Detection Kit
Core advantage: Enhanced linearity at high concentrations (IC50 40.1 nM), resistant to complex sample interference.
Typical applications: Extreme pathological models (e.g., tumors), constitutively active mutants, and other special scenarios.